
The Knee joint is one of the largest joints in the body in which the thigh bone femur articulates with the leg bone tibia and the knee cap (patella).The femur glides and rotates over tibia and the ligaments around it maintain a harmonious joint movement. The articular cartilage covering the bone surfaces works as a cushion allowing smooth painfree motion.
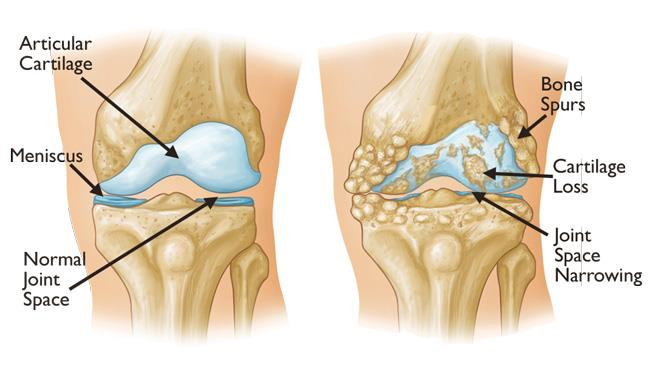
Normal and arthritic knee
In patients with degenerative arthritis this cartilage acting like cushion gets destroyed and causes friction in movement causing pain in walking, climbing stairs and other load bearing activites. The joint may also be damaged because of fractures, ligament injury, alignment problems and inflammatory arthritis. Treatment of arthritis includes medications, intraarticular injections, activity modifications, joint preserving surgery and using walking supports. If the symptoms still persist or the xray shows complete loss of articular cartilage (cushion) bone on bone appearance you will need a knee replacement. In knee replacement the diseased joint is resurfaced with metal and plastic components serving as artificial cushions and allowing painfree movement.

Total knee replacement
Knee Replacement Implant:
The knee replacement material may be of cobalt chrome, titanium or plastic and are fixed to the bone using a special kind of cement. The femoral head may be of cobalt chrome or oxynium coated to decrease wear of the polyethylene liner.
Knee replacement is a very rewarding surgery and given the patient a painfree mobile joint again. However realistic expectations are necessary. Patient can recover to the point where he was before the disease process began. You can even jog or walk fast with the artificial joint but should be in a good physical shape to do that. High impact activities are discouraged as they cause accelerated wear and loosening of the prosthetic joint like any other machinery. Also the patient should not sit or squat on ground as it may cause dislocation of the joint.
SURGERY:
Surgery is generally done in spinal anaethesia and takes a few hours to perform. The surgery is performed using reduced tissue trauma technique using a minimally invasive technique that decreases postoperative pain and causes early recovery for the patient.
Like any surgery it may have complications related to anaesthesia, bleeding , infection, blood clots in the legs or lungs, revision surgery, nerve injury causing numbness or weakness. However with proper precautions the complication rate is below 5%.
After the surgery patient may be discharged after 4-5 days. The patient is generally allowed partial weight bearing in a day or two depending on his pain and recovery. The stitches are generally removed at 15 days. Physiotherapy is started on Day 2 after surgery and gradually progressed to walking with walker and with cane by the end of 1 month depending on patient age and strength. Physiotherapy is continued till the patient gains full movement and strength of the leg.
